ISRO, 28th August 2023:
ISRO to Go for Sun, Aditya L1 Satellite to Sun
ISRO to go for Sun next month with Aditya-L1 satellite
Mission To Sun ☀️
India first Space Observatory mission to Sun #AdityaL1 will take 109 day to reach 1.5 million Km from Earth.
It’s life Span will be more then 5 Years & will help #ISRO to study Sun.
It will be launched either on Sep 2nd or 4th depend on weather 🇮🇳

ISRO to Go for Sun, Aditya L1 Satellite to Sun
ISRO to Go for Sun, Aditya L1 Satellite to Sun
ISRO ADITYA-L1 MISSION: THE FIRST OBSERVATORY-CLASS SPACE-BASED SOLAR MISSION FROM INDIA
Chandrayaan 3 has successfully soft-landed on the moon
Aditya L1 shall be the first space based Indian mission to study the Sun. The spacecraft shall be placed in a halo orbit around the Lagrange point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system, which is about 1.5 million km from the Earth.

ISRO to Go for Sun, Aditya L1 Satellite to Sun
ISRO to Go for Sun, Aditya L1 Satellite to Sun
SCIENCE OBJECTIVES: The major science objectives of mission are:
1) Study of Solar upper atmospheric (chromosphere and corona) dynamics.
2) Study of chromospheric and coronal heating, physics of the partially ionized plasma, initiation of the coronal mass ejections, & flares.
3) Observe the in-situ particle and plasma environment providing data for the study of particle dynamics from the Sun.
4) Physics of solar corona and its heating mechanism. 5) Diagnostics of the coronal and coronal loops plasma: Temperature, velocity and density.
6) Development, dynamics and origin of CMEs.
How Congress used to treat ISRO
7) Identify the sequence of processes that occur at multiple layers (chromosphere, base and extended corona) which eventually leads to solar eruptive events.
8) Magnetic field topology and magnetic field measurements in the solar corona .
9) Drivers for space weather (origin, composition and dynamics of solar wind .
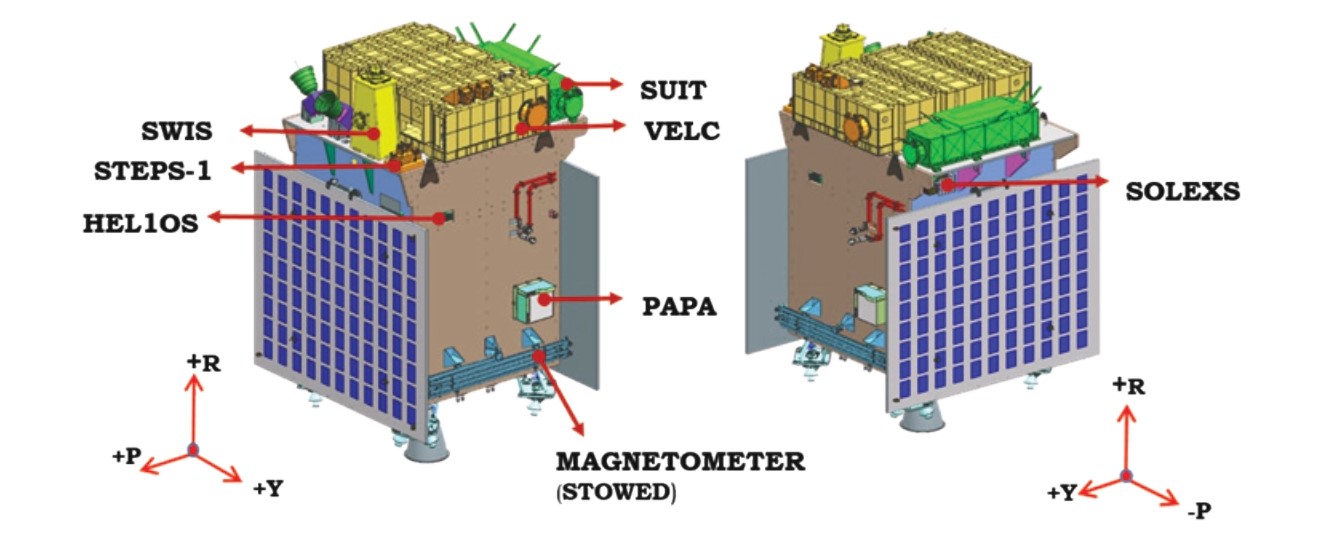
ADITYA-L1 PAYLOADS:
Remote Sensing Payloads:
1) Visible Emission Line Coronagraph(VELC)
2) Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT)
3) Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS) 4) High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS)
In-situ Payloads:
1) Aditya Solar wind Particle Experiment(ASPEX)
2) Plasma Analyser Package For Aditya (PAPA)
3) Advanced Tri-axial High Resolution Digital Magnetometers
Ministry of Minority Affairs Banned the Fake Scholarship Beneficiaries and Institutions
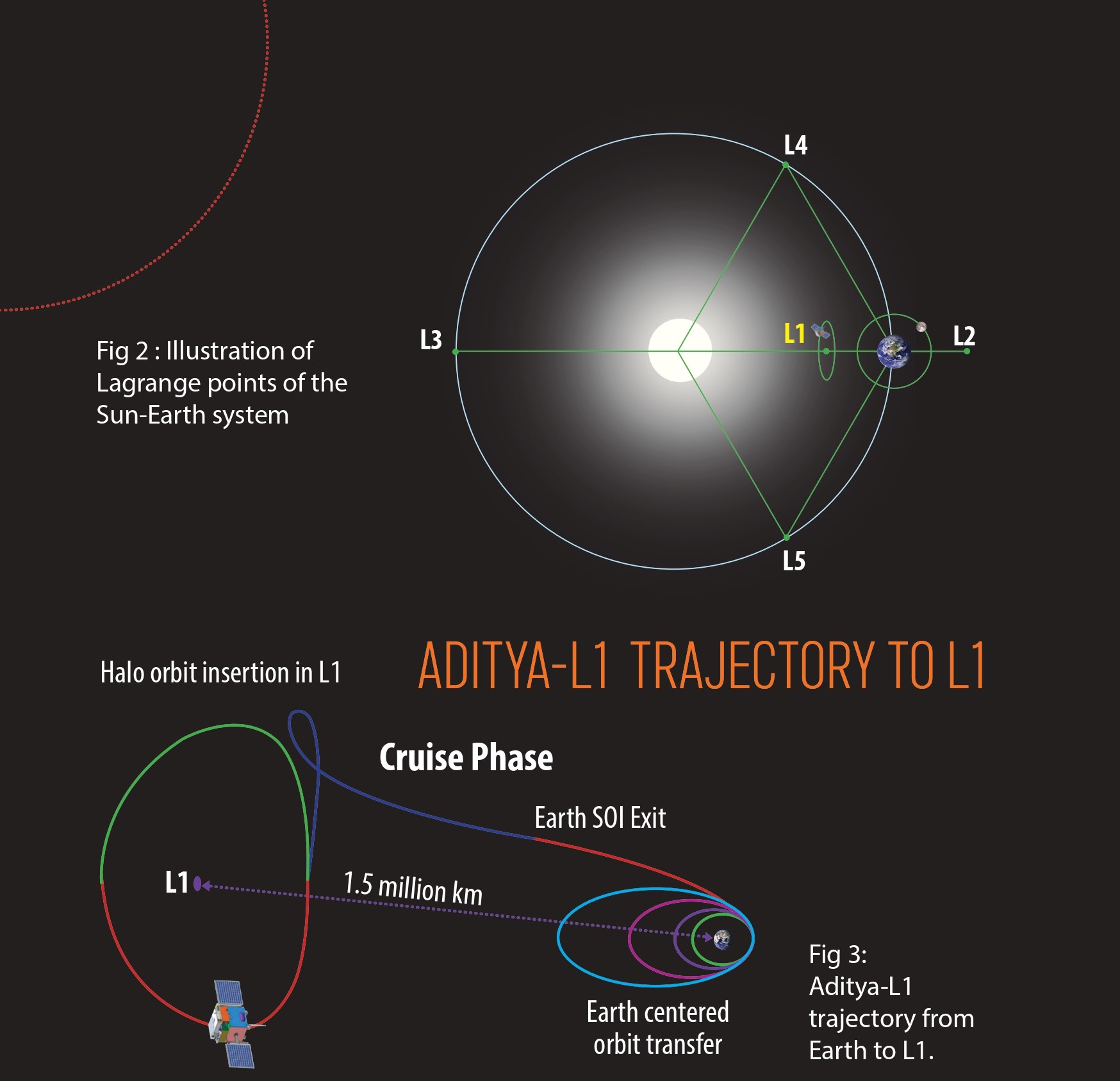
ADITYA-L1 TRAJECTORY TO L1:
LAGRANGE POINTS For a two body gravitational system, the Lagrange Points are the positions in space where a small object tends to stay, if put there. These points in space for a 2 body systems such as Sun & Earth can be used by spacecraft to remain
ISRO to Go for Sun, Aditya L1 Satellite to Sun
at these positions with reduced fuel consumption. Technically at Lagrange point, the gravitational pull of the 2 large bodies equals the necessary centripetal force required for a small object to move with them.
For 2 body gravitational systems, there are total 5 Lagrange pts denoted as L1, L2, L3, L4 & L5.
The Lagrange points for Sun-Earth system are shown in the figure. The Lagrange point L1 lies between Sun-Earth line. The distance of L1 from Earth is approximately 1% of the Earth-Sun distance.